List of network system messages
There are three types of messages with overlapping message ids:
system messages,
game messages and
control messages
This list is only covering system messages.
<heinrich5991> ChillerDragon: the system messages are part of the engine and do not really know anything about the game
<heinrich5991> both snapshots and inputs are transmitted in a way that makes the engine more or less oblivious of its contents
When the client and server exchange packets. An integer field which usually does not exceed one byte. Is indicating which type of message was sent. This field is called the message id. These message ids are defined in src/engine/shared/protocol.h and their payload is defined where they are sent and received. There can be multiple messages in so called chunks in one teeworlds packet.
In the list below you will find those message. With their name, id and payload.
NETMSG_NULL
| Message ID: | 0 |
|---|
NETMSG_INFO
| Sender: | Client |
|---|---|
| Recipient: | Server |
| Message ID: | 1 |
| Response to: | NET_CTRLMSG_ACCEPT |
| Expected response: | NETMSG_MAP_CHANGE |
| Argument name | Type | Note |
|---|---|---|
| Net Version | String |
The official name is "NetVersion" but a more fitting name in my opinion would be "Protocol Version".
The variable GAME_NETVERSION always expands to "0.7 802f1be60a05665f"If the server gets another string it actually rejects the connection. This is what prohibits 0.6 clients to join 0.7 servers. |
| Password | String |
If the config option password is set on the server. This password has to match to join the server.
The vanilla 0.7 client always sends the last used passwords to all servers no matter if they expect a password or not.
And servers simply ignore this field if no password is expected.
|
| Client Version | Int | Another version field which does not have to match the servers version to establish a connection. The first net version field makes sure that client and server use the same major protocol and are compatible. This "Client Version" field then informs the server about the clients minor version. The server can use it to activate some non protocol breaking features that were introduced in minor releases. |
Sent by the client in CClient::SendInfo()
void CClient::SendInfo()
{
// restore password of favorite if possible
const char *pPassword = m_ServerBrowser.GetFavoritePassword(m_aServerAddressStr);
if(!pPassword)
pPassword = Config()->m_Password;
str_copy(m_aServerPassword, pPassword, sizeof(m_aServerPassword));
CMsgPacker Msg(NETMSG_INFO, true);
Msg.AddString(GameClient()->NetVersion(), 128);
Msg.AddString(m_aServerPassword, 128);
Msg.AddInt(GameClient()->ClientVersion());
SendMsg(&Msg, MSGFLAG_VITAL|MSGFLAG_FLUSH);
}
Received by the server in
CServer::ProcessClientPacket(CNetChunk *pPacket)
if(Msg == NETMSG_INFO)
{
if((pPacket->m_Flags&NET_CHUNKFLAG_VITAL) != 0 && m_aClients[ClientID].m_State == CClient::STATE_AUTH)
{
const char *pVersion = Unpacker.GetString(CUnpacker::SANITIZE_CC);
if(str_comp(pVersion, GameServer()->NetVersion()) != 0)
{
// wrong version
char aReason[256];
str_format(aReason, sizeof(aReason), "Wrong version. Server is running '%s' and client '%s'", GameServer()->NetVersion(), pVersion);
m_NetServer.Drop(ClientID, aReason);
return;
}
const char *pPassword = Unpacker.GetString(CUnpacker::SANITIZE_CC);
if(Config()->m_Password[0] != 0 && str_comp(Config()->m_Password, pPassword) != 0)
{
// wrong password
m_NetServer.Drop(ClientID, "Wrong password");
return;
}
m_aClients[ClientID].m_Version = Unpacker.GetInt();
m_aClients[ClientID].m_State = CClient::STATE_CONNECTING;
SendMap(ClientID);
}
}
NETMSG_MAP_CHANGE
| Sender: | Server |
|---|---|
| Recipient: | Client |
| Message ID: | 2 |
| Response to: | NETMSG_INFO |
| Expected response: |
NETMSG_REQUEST_MAP_DATA | NETMSG_READY |
| Argument name | Type | Note |
|---|---|---|
| Map name | String | Name of the map. The client will use this name and the crc to lookup if it already has the map in the downloadedmaps/ folder |
| Crc | Int | The Cyclic redundancy check (Crc) hash is used to differentiate between different maps that share the same name. |
| Map size | Int | The size of the map in bytes. |
| Chunks per request | Int |
The value is coming from the servers config option sv_map_download_speed
|
| Chunk size | Int |
Since the map download chunks contain an unterminated raw data field
the server is informing the client here how big that data field is.
It is sending MAP_CHUNK_SIZE which is defined as
MAP_CHUNK_SIZE=NET_MAX_PAYLOAD-NET_MAX_CHUNKHEADERSIZE-4
which evalutes to 1384.
So on a unmodified vanilla server this will always be the fixed value
1384 but custom servers could change it and the client
should technically support that.
|
| Map sha256 | Raw |
Since crc is a weak hashing algorithm this new field was added
to avoid hash collisions and better differentiate maps with the same name.
It was added as a security update since the crc collision was attackable.
And one could trick clients into thinking they know a certain map already.
There is no length field for this raw field. Client and server use the fixed pre agreed size SHA256_DIGEST_LENGTH (32)
|
See the map_download section for a higher level overview.
Sent by the server in CServer::SendMap(int ClientID)
CMsgPacker Msg(NETMSG_MAP_CHANGE, true);
Msg.AddString(GetMapName(), 0);
Msg.AddInt(m_CurrentMapCrc);
Msg.AddInt(m_CurrentMapSize);
Msg.AddInt(m_MapChunksPerRequest);
Msg.AddInt(MAP_CHUNK_SIZE);
Msg.AddRaw(&m_CurrentMapSha256, sizeof(m_CurrentMapSha256));
SendMsg(&Msg, MSGFLAG_VITAL|MSGFLAG_FLUSH, ClientID);
Unpacked by the client in
CClient::ProcessServerPacket(CNetChunk *pPacket)
const char *pMap = Unpacker.GetString(CUnpacker::SANITIZE_CC|CUnpacker::SKIP_START_WHITESPACES);
int MapCrc = Unpacker.GetInt();
int MapSize = Unpacker.GetInt();
int MapChunkNum = Unpacker.GetInt();
int MapChunkSize = Unpacker.GetInt();
if(Unpacker.Error())
return;
const SHA256_DIGEST *pMapSha256 = (const SHA256_DIGEST *)Unpacker.GetRaw(sizeof(*pMapSha256));
NETMSG_MAP_DATA
| Sender: | Server |
|---|---|
| Recipient: | Client |
| Message ID: | 3 |
| Response to: | NETMSG_REQUEST_MAP_DATA |
| Expected response: | NETMSG_READY |
| Argument name | Type | Note |
|---|---|---|
| Map data | Raw |
This message contains individual pieces of the whole map file.
They will be split in chunks of size MAP_CHUNK_SIZE
usually 1384 or a custom value provided by the server
in the chunk size field of
the NETMSG_MAP_CHANGE message
|
If the client did send a NETMSG_REQUEST_MAP_DATA. The server will respond with those map chunk messages in CServer::ProcessClientPacket(CNetChunk *pPacket)
else if(Msg == NETMSG_REQUEST_MAP_DATA)
{
if((pPacket->m_Flags&NET_CHUNKFLAG_VITAL) != 0 && (m_aClients[ClientID].m_State == CClient::STATE_CONNECTING || m_aClients[ClientID].m_State == CClient::STATE_CONNECTING_AS_SPEC))
{
int ChunkSize = MAP_CHUNK_SIZE;
// send map chunks
for(int i = 0; i < m_MapChunksPerRequest && m_aClients[ClientID].m_MapChunk >= 0; ++i)
{
int Chunk = m_aClients[ClientID].m_MapChunk;
int Offset = Chunk * ChunkSize;
// check for last part
if(Offset+ChunkSize >= m_CurrentMapSize)
{
ChunkSize = m_CurrentMapSize-Offset;
m_aClients[ClientID].m_MapChunk = -1;
}
else
m_aClients[ClientID].m_MapChunk++;
CMsgPacker Msg(NETMSG_MAP_DATA, true);
Msg.AddRaw(&m_pCurrentMapData[Offset], ChunkSize);
SendMsg(&Msg, MSGFLAG_VITAL|MSGFLAG_FLUSH, ClientID);
if(Config()->m_Debug)
{
char aBuf[64];
str_format(aBuf, sizeof(aBuf), "sending chunk %d with size %d", Chunk, ChunkSize);
Console()->Print(IConsole::OUTPUT_LEVEL_DEBUG, "server", aBuf);
}
}
}
}
The client then unpacks them in
CClient::ProcessServerPacket(CNetChunk *pPacket)
else if((pPacket->m_Flags&NET_CHUNKFLAG_VITAL) != 0 && Msg == NETMSG_MAP_DATA)
{
if(!m_MapdownloadFileTemp)
return;
int Size = minimum(m_MapDownloadChunkSize, m_MapdownloadTotalsize-m_MapdownloadAmount);
const unsigned char *pData = Unpacker.GetRaw(Size);
// [..]
The client uses the m_MapDownloadChunkSize
as size of the raw field. This variable was set to the value
of the Chunk Size field from the
NETMSG_MAP_CHANGE message.
See the map_download section for a higher level overview.
NETMSG_SERVERINFO
| Sender: | Server |
|---|---|
| Recipient: | Client |
| Message ID: | 4 |
| Response to: |
NETMSG_ENTERGAME | NETMSG_RCON_CMD ( sv_name, password, sv_max_clients)
|
| Expected response: | None |
| Argument name | Type | Note |
|---|---|---|
| Game version | String | TODO |
| Name | String | TODO |
| Hostname | String | TODO |
| Map name | String | TODO |
| Game type | String | TODO |
| Flags | Int |
There are only two possible flags
SERVERINFO_FLAG_PASSWORD (1)
and
SERVERINFO_FLAG_TIMESCORE (2)
|
| Skill level | Int |
0 is meant to be used for public servers where anyone is welcome.
And 2 is meant to be used for more elite servers where beginners are not welcome.
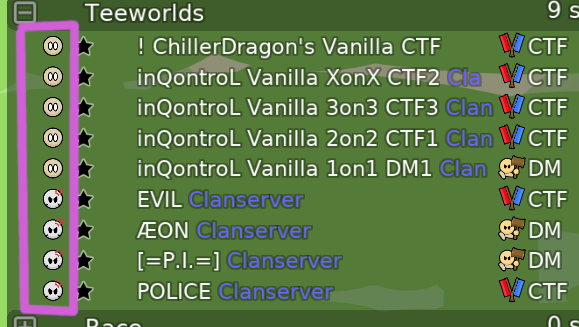
|
| Player count | Int | TODO |
| Player slots | Int | TODO |
| Client count | Int | TODO |
| Max clients | Int | TODO |
The server sends the server info to every client that joins. After the client did send the NETMSG_ENTERGAME message. Or if a server admin does change the server info it will be resend it to all clients. By setting the rcon variables
sv_name, password or sv_max_clients.It is sent via the function CServer::SendServerInfo(int ClientID)
void CServer::SendServerInfo(int ClientID)
{
CMsgPacker Msg(NETMSG_SERVERINFO, true);
GenerateServerInfo(&Msg, -1);
if(ClientID == -1)
{
for(int i = 0; i < MAX_CLIENTS; i++)
{
if(m_aClients[i].m_State != CClient::STATE_EMPTY)
SendMsg(&Msg, MSGFLAG_VITAL|MSGFLAG_FLUSH, i);
}
}
else if(ClientID >= 0 && ClientID < MAX_CLIENTS && m_aClients[ClientID].m_State != CClient::STATE_EMPTY)
SendMsg(&Msg, MSGFLAG_VITAL|MSGFLAG_FLUSH, ClientID);
}
It will be unpacked by the client in
CClient::ProcessServerPacket(CNetChunk *pPacket)
else if((pPacket->m_Flags&NET_CHUNKFLAG_VITAL) != 0 && Msg == NETMSG_SERVERINFO)
{
CServerInfo Info = {0};
net_addr_str(&pPacket->m_Address, Info.m_aAddress, sizeof(Info.m_aAddress), true);
if(!UnpackServerInfo(&Unpacker, &Info, 0) && !Unpacker.Error())
{
SortClients(&Info);
mem_copy(&m_CurrentServerInfo, &Info, sizeof(m_CurrentServerInfo));
m_CurrentServerInfo.m_NetAddr = m_ServerAddress;
}
}
NETMSG_CON_READY
| Sender: | Server |
|---|---|
| Recipient: | Client |
| Message ID: | 5 |
| Response to: | NETMSG_READY |
| Expected response: | NETMSGTYPE_CL_STARTINFO |
| Argument name | Type | Note |
|---|---|---|
| None | ||
After the server did receive a NETMSG_READY from the client. It will respond with this message in CServer::ProcessClientPacket(CNetChunk *pPacket)
else if(Msg == NETMSG_READY)
{
if((pPacket->m_Flags&NET_CHUNKFLAG_VITAL) != 0 && (m_aClients[ClientID].m_State == CClient::STATE_CONNECTING || m_aClients[ClientID].m_State == CClient::STATE_CONNECTING_AS_SPEC))
{
char aAddrStr[NETADDR_MAXSTRSIZE];
net_addr_str(m_NetServer.ClientAddr(ClientID), aAddrStr, sizeof(aAddrStr), true);
char aBuf[256];
str_format(aBuf, sizeof(aBuf), "player is ready. ClientID=%d addr=%s", ClientID, aAddrStr);
Console()->Print(IConsole::OUTPUT_LEVEL_ADDINFO, "server", aBuf);
bool ConnectAsSpec = m_aClients[ClientID].m_State == CClient::STATE_CONNECTING_AS_SPEC;
m_aClients[ClientID].m_State = CClient::STATE_READY;
GameServer()->OnClientConnected(ClientID, ConnectAsSpec);
SendConnectionReady(ClientID);
}
}
If the client does receive it it will call GameClient()->OnConnected()
else if((pPacket->m_Flags&NET_CHUNKFLAG_VITAL) != 0 && Msg == NETMSG_CON_READY)
{
GameClient()->OnConnected();
}
void CGameClient::OnConnected()
{
m_Layers.Init(Kernel());
m_Collision.Init(Layers());
for(int i = 0; i < m_All.m_Num; i++)
{
m_All.m_paComponents[i]->OnMapLoad();
m_All.m_paComponents[i]->OnReset();
}
m_ServerMode = SERVERMODE_PURE;
// send the inital info
SendStartInfo();
}
void CGameClient::SendStartInfo()
{
CNetMsg_Cl_StartInfo Msg;
Msg.m_pName = Config()->m_PlayerName;
Msg.m_pClan = Config()->m_PlayerClan;
Msg.m_Country = Config()->m_PlayerCountry;
for(int p = 0; p < NUM_SKINPARTS; p++)
{
Msg.m_apSkinPartNames[p] = CSkins::ms_apSkinVariables[p];
Msg.m_aUseCustomColors[p] = *CSkins::ms_apUCCVariables[p];
Msg.m_aSkinPartColors[p] = *CSkins::ms_apColorVariables[p];
}
Client()->SendPackMsg(&Msg, MSGFLAG_VITAL|MSGFLAG_FLUSH);
}
NETMSG_SNAP
| Sender: | Server |
|---|---|
| Recipient: | Client |
| Message ID: | 6 |
| Response to: | Updates in the world |
| Expected response: | The client acknowledges the Game tick in the message NETMSG_INPUT |
| Argument name | Type | Note |
|---|---|---|
| Game tick | Int | The tick at which this snapshot happens. Will be acknowledged by the client in the input message. Read more about ticks and delta ticks here |
| Delta tick | Int | The base snapshot game tick which the delta was created from. Will be -1 for the first snapshot signaling it is a delta based on the empty snapshot. Read more about delta ticks here |
| Num parts | Int |
Indicates the total amount of parts for this snapshot. The current part is set in the Part field.
The client is supposed to collect the payload and concatinate it locally and only if the last part is received it should parse the snapshot.
Where last part is defined as Part == Num Parts - 1.
So if Num Parts is set to 2 the first Part will be 0 and the second (last) will be 1.
|
| Part | Int | 0 based index for Num Parts. |
| Crc | Int |
The crc (cyclic redundancy check) is used as a checksum verifying the integrity of the snapshot.
It is all snapshot item payloads summed together into one 32 bit integer.
The reference implementation might overflow the crc and so should you to match the exact value.
More details on how to calculate the crc can be seen in the
teeframe documentation.
Important to understand is that the crc is not applied to only the snap items sent in this net message but the full snapshot. Every snap msg is just a delta that might add or remove items from a previous snapshot. So if the client already knows about a snapshot with 3 items and then another NETMSG_SNAP comes in with 3 additional items as payload the crc has to be calculated on all 6 items that are now in the fully unpacked snapshot. |
| Part size | Int | The size of this part. Meaning the size in bytes of the next raw data field. |
| Data | Raw |
The partial snapshot data. It should be only processed when all
Num parts are assembled together.
The snapshot data. Which is a bunch of packed ints. The first is the amount of removed items. The second is the amount of item deltas. The third a unused zero byte. Then there are "amount of removed items" repeated integers identifying the deleted items. Followed by "amount of item deltas" repeated snap items You can read more about snap items and the structure of this data field in the snap items section. A full overview about the entire snap payload (all data sections from part 0 till num parts combined) can be found here |
Will be sent by the server to every client if there is new snap data. If the data is small enough to fit in a single message it will use NETMSG_SNAPSINGLE instead.
NETMSG_SNAPEMPTY
| Sender: | Server |
|---|---|
| Recipient: | Client |
| Message ID: | 7 |
| Response to: | None |
| Expected response: | None |
| Argument name | Type | Note |
|---|---|---|
| Game tick | Int | TODO |
| Delta tick | Int | The base snapshot game tick which the delta was created from. Will be -1 for the first snapshot signaling it is a delta based on the empty snapshot. |
CMsgPacker Msg(NETMSG_SNAPEMPTY, true);
Msg.AddInt(m_CurrentGameTick);
Msg.AddInt(m_CurrentGameTick-DeltaTick);
SendMsg(&Msg, MSGFLAG_FLUSH, i);
NETMSG_SNAPSINGLE
| Sender: | Server |
|---|---|
| Recipient: | Client |
| Message ID: | 8 |
| Response to: | Updates in the world |
| Expected response: | The client acknowledges the Game tick in the message NETMSG_INPUT |
| Argument name | Type | Note |
|---|---|---|
| Game tick | Int | TODO |
| Delta tick | Int | The base snapshot game tick which the delta was created from. Will be -1 for the first snapshot signaling it is a delta based on the empty snapshot. |
| Crc | Int | The crc is a checksum. More details here. |
| Part size | Int | The size of this part. Meaning the size in bytes of the next raw data field. |
| Data | Raw |
The snapshot data. Which is a bunch of packed ints.
The first is the amount of removed items.
The second is the amount of item deltas.
The third a unused zero byte.
Then there are "amount of removed items" repeated integers
identifying the deleted items. Followed by "amount of item deltas" repeated snap items
You can read more about snap items and the structure
of this data field in the
snap items
section.
A full overview about the entire snap payload can be found here |
NETMSG_SNAPSMALL
| Sender: | Server |
|---|---|
| Recipient: | Client |
| Message ID: | 9 |
| Response to: | None |
| Expected response: | None |
NETMSG_INPUTTIMING
| Sender: | Server |
|---|---|
| Recipient: | Client |
| Message ID: | 10 |
| Response to: | NETMSG_INPUT |
| Expected response: | None |
| Argument name | Type | Note |
|---|---|---|
| Intended tick | Int | TODO |
| Time left | Int | TODO |
The server responds this to all the input messages from the clients in CServer::ProcessClientPacket(CNetChunk *pPacket)
// add message to report the input timing
// skip packets that are old
if(IntendedTick > m_aClients[ClientID].m_LastInputTick)
{
int TimeLeft = ((TickStartTime(IntendedTick)-Now)*1000) / time_freq();
CMsgPacker Msg(NETMSG_INPUTTIMING, true);
Msg.AddInt(IntendedTick);
Msg.AddInt(TimeLeft);
SendMsg(&Msg, 0, ClientID);
}
The client uses this data to correct its prediction in
CClient::ProcessServerPacket(CNetChunk *pPacket)
else if(Msg == NETMSG_INPUTTIMING)
{
int InputPredTick = Unpacker.GetInt();
int TimeLeft = Unpacker.GetInt();
// adjust our prediction time
int64 Target = 0;
for(int k = 0; k < 200; k++)
{
if(m_aInputs[k].m_Tick == InputPredTick)
{
Target = m_aInputs[k].m_PredictedTime + (time_get() - m_aInputs[k].m_Time);
Target = Target - (int64)(((TimeLeft-PREDICTION_MARGIN)/1000.0f)*time_freq());
break;
}
}
if(Target)
m_PredictedTime.Update(&m_InputtimeMarginGraph, Target, TimeLeft, 1);
}
NETMSG_RCON_AUTH_ON
| Sender: | Server |
|---|---|
| Recipient: | Client |
| Message ID: | 11 |
| Response to: | NETMSG_RCON_AUTH |
| Expected response: | None |
| Argument name | Type | Note |
|---|---|---|
| None | ||
else if(Config()->m_SvRconPassword[0] && str_comp(pPw, Config()->m_SvRconPassword) == 0)
{
CMsgPacker Msg(NETMSG_RCON_AUTH_ON, true);
SendMsg(&Msg, MSGFLAG_VITAL, ClientID);
else if(Config()->m_SvRconModPassword[0] && str_comp(pPw, Config()->m_SvRconModPassword) == 0)
{
CMsgPacker Msg(NETMSG_RCON_AUTH_ON, true);
SendMsg(&Msg, MSGFLAG_VITAL, ClientID);
The client sets m_RconAuthed to true (1) on receival.
Which enables the rcon prompt in the client UI.
else if((pPacket->m_Flags&NET_CHUNKFLAG_VITAL) != 0 && Msg == NETMSG_RCON_AUTH_ON)
{
m_RconAuthed = 1;
m_UseTempRconCommands = 1;
}
NETMSG_RCON_AUTH_OFF
| Sender: | Server |
|---|---|
| Recipient: | Client |
| Message ID: | 12 |
| Response to: | NETMSG_RCON_CMD (logout) |
| Expected response: | None |
| Argument name | Type | Note |
|---|---|---|
| None | ||
logout rcon command.
void CServer::ConLogout(IConsole::IResult *pResult, void *pUser)
{
CServer *pServer = (CServer *)pUser;
if(pServer->m_RconClientID >= 0 && pServer->m_RconClientID < MAX_CLIENTS &&
pServer->m_aClients[pServer->m_RconClientID].m_State != CServer::CClient::STATE_EMPTY)
{
CMsgPacker Msg(NETMSG_RCON_AUTH_OFF, true);
pServer->SendMsg(&Msg, MSGFLAG_VITAL, pServer->m_RconClientID);
pServer->m_aClients[pServer->m_RconClientID].m_Authed = AUTHED_NO;
pServer->m_aClients[pServer->m_RconClientID].m_AuthTries = 0;
pServer->m_aClients[pServer->m_RconClientID].m_pRconCmdToSend = 0;
pServer->m_aClients[pServer->m_RconClientID].m_pMapListEntryToSend = 0;
pServer->SendRconLine(pServer->m_RconClientID, "Logout successful.");
char aBuf[32];
str_format(aBuf, sizeof(aBuf), "ClientID=%d logged out", pServer->m_RconClientID);
pServer->Console()->Print(IConsole::OUTPUT_LEVEL_STANDARD, "server", aBuf);
}
}
If the client gets this message it sets m_RconAuthed to false (0)
which deactivates the rcon prompt in the client UI.
It also deletes all rcon commands the server sent to the client during the time
the client was authed.
else if((pPacket->m_Flags&NET_CHUNKFLAG_VITAL) != 0 && Msg == NETMSG_RCON_AUTH_OFF)
{
m_RconAuthed = 0;
if(m_UseTempRconCommands)
m_pConsole->DeregisterTempAll();
m_UseTempRconCommands = 0;
m_pConsole->DeregisterTempMapAll();
}
NETMSG_RCON_LINE
| Sender: | Server |
|---|---|
| Recipient: | Client |
| Message ID: | 13 |
| Response to: | NETMSG_RCON_CMD | NETMSG_RCON_AUTH |
| Expected response: | None |
| Argument name | Type | Note |
|---|---|---|
| Line | String | Text to be printed in the clients remote console |
All messages that show up in the clients rcon console are coming from this message. They are send by the server in CServer::SendRconLine(int ClientID, const char *pLine)
void CServer::SendRconLine(int ClientID, const char *pLine)
{
CMsgPacker Msg(NETMSG_RCON_LINE, true);
Msg.AddString(pLine, 512);
SendMsg(&Msg, MSGFLAG_VITAL, ClientID);
}
If the client gets this packet. It adds the payload (line) into the console log where the rendere can pick it up if the user opens the rcon console.
else if((pPacket->m_Flags&NET_CHUNKFLAG_VITAL) != 0 && Msg == NETMSG_RCON_LINE)
{
const char *pLine = Unpacker.GetString();
if(Unpacker.Error() == 0)
GameClient()->OnRconLine(pLine);
}
NETMSG_RCON_CMD_ADD
| Sender: | Server |
|---|---|
| Recipient: | Client |
| Message ID: | 14 |
| Response to: | NETMSG_RCON_AUTH |
| Expected response: | None |
| Argument name | Type | Note |
|---|---|---|
| Name | String | TODO |
| Help | String | TODO |
| Params | String | TODO |
void CServer::SendRconCmdAdd(const IConsole::CCommandInfo *pCommandInfo, int ClientID)
{
CMsgPacker Msg(NETMSG_RCON_CMD_ADD, true);
Msg.AddString(pCommandInfo->m_pName, IConsole::TEMPCMD_NAME_LENGTH);
Msg.AddString(pCommandInfo->m_pHelp, IConsole::TEMPCMD_HELP_LENGTH);
Msg.AddString(pCommandInfo->m_pParams, IConsole::TEMPCMD_PARAMS_LENGTH);
SendMsg(&Msg, MSGFLAG_VITAL, ClientID);
}
The client then receives them in
CClient::ProcessServerPacket(CNetChunk *pPacket)
where it stores them into the autocompletion list used by the remote console UI.
else if((pPacket->m_Flags&NET_CHUNKFLAG_VITAL) != 0 && Msg == NETMSG_RCON_CMD_ADD)
{
const char *pName = Unpacker.GetString(CUnpacker::SANITIZE_CC);
const char *pHelp = Unpacker.GetString(CUnpacker::SANITIZE_CC);
const char *pParams = Unpacker.GetString(CUnpacker::SANITIZE_CC);
if(Unpacker.Error() == 0)
m_pConsole->RegisterTemp(pName, pParams, CFGFLAG_SERVER, pHelp);
}
NETMSG_RCON_CMD_REM
| Sender: | Server |
|---|---|
| Recipient: | Client |
| Message ID: | 15 |
| Response to: | NETMSG_RCON_CMD (mod_command) |
| Expected response: | None |
| Argument name | Type | Note |
|---|---|---|
| Name | String | Name of command to be deleted |
mod_command
).
The method sending this message is
SendRconCmdRem()
void CServer::SendRconCmdRem(const IConsole::CCommandInfo *pCommandInfo, int ClientID)
{
CMsgPacker Msg(NETMSG_RCON_CMD_REM, true);
Msg.AddString(pCommandInfo->m_pName, 256);
SendMsg(&Msg, MSGFLAG_VITAL, ClientID);
}
If the client receives it it will remove the command with the given name
from its list of known commands in
CClient::ProcessServerPacket(CNetChunk *pPacket)
else if((pPacket->m_Flags&NET_CHUNKFLAG_VITAL) != 0 && Msg == NETMSG_RCON_CMD_REM)
{
const char *pName = Unpacker.GetString(CUnpacker::SANITIZE_CC);
if(Unpacker.Error() == 0)
m_pConsole->DeregisterTemp(pName);
}
NETMSG_AUTH_CHALLANGE
| Sender: | Unused |
|---|---|
| Recipient: | Unused |
| Message ID: | 16 |
| Response to: | Unused |
| Expected response: | Unused |
| Argument name | Type | Note |
|---|---|---|
| Unused | ||
Note challenge is misspelled (here to optimize search results)
NETMSG_AUTH_RESULT
| Sender: | Unused |
|---|---|
| Recipient: | Unused |
| Message ID: | 17 |
| Response to: | Unused |
| Expected response: | Unused |
| Argument name | Type | Note |
|---|---|---|
| Unused | ||
NETMSG_READY
| Sender: | Client |
|---|---|
| Recipient: | Server |
| Message ID: | 18 |
| Response to: | NETMSG_MAP_CHANGE | NETMSG_MAP_DATA |
| Expected response: |
NETMSG_CON_READY & NETMSGTYPE_SV_MOTD & NETMSGTYPE_SV_SERVERSETTINGS |
| Argument name | Type | Note |
|---|---|---|
| None | ||
void CClient::SendReady()
{
CMsgPacker Msg(NETMSG_READY, true);
SendMsg(&Msg, MSGFLAG_VITAL|MSGFLAG_FLUSH);
}
The server calls
SendConnectionReady(ClientID);
when it receives this message in the
CServer::ProcessClientPacket(CNetChunk *pPacket)
method
else if(Msg == NETMSG_READY)
{
if((pPacket->m_Flags&NET_CHUNKFLAG_VITAL) != 0 && (m_aClients[ClientID].m_State == CClient::STATE_CONNECTING || m_aClients[ClientID].m_State == CClient::STATE_CONNECTING_AS_SPEC))
{
char aAddrStr[NETADDR_MAXSTRSIZE];
net_addr_str(m_NetServer.ClientAddr(ClientID), aAddrStr, sizeof(aAddrStr), true);
char aBuf[256];
str_format(aBuf, sizeof(aBuf), "player is ready. ClientID=%d addr=%s", ClientID, aAddrStr);
Console()->Print(IConsole::OUTPUT_LEVEL_ADDINFO, "server", aBuf);
bool ConnectAsSpec = m_aClients[ClientID].m_State == CClient::STATE_CONNECTING_AS_SPEC;
m_aClients[ClientID].m_State = CClient::STATE_READY;
GameServer()->OnClientConnected(ClientID, ConnectAsSpec);
SendConnectionReady(ClientID);
}
}
The
SendConnectionReady(ClientID);
then sends the NETMSG_CON_READY as a response to the client.
NETMSG_ENTERGAME
| Sender: | Client |
|---|---|
| Recipient: | Server |
| Message ID: | 19 |
| Response to: | NETMSGTYPE_SV_READYTOENTER |
| Expected response: |
NETMSGTYPE_SV_COMMANDINFO & NETMSG_SERVERINFO & NETMSGTYPE_SV_GAMEINFO & NETMSGTYPE_SV_CLIENTINFO |
| Argument name | Type | Note |
|---|---|---|
| None | ||
void CClient::SendEnterGame()
{
CMsgPacker Msg(NETMSG_ENTERGAME, true);
SendMsg(&Msg, MSGFLAG_VITAL|MSGFLAG_FLUSH);
}
The server processes this message in
CServer::ProcessClientPacket(CNetChunk *pPacket)
else if(Msg == NETMSG_ENTERGAME)
{
if((pPacket->m_Flags&NET_CHUNKFLAG_VITAL) != 0 && m_aClients[ClientID].m_State == CClient::STATE_READY && GameServer()->IsClientReady(ClientID))
{
char aAddrStr[NETADDR_MAXSTRSIZE];
net_addr_str(m_NetServer.ClientAddr(ClientID), aAddrStr, sizeof(aAddrStr), true);
char aBuf[256];
str_format(aBuf, sizeof(aBuf), "player has entered the game. ClientID=%d addr=%s", ClientID, aAddrStr);
Console()->Print(IConsole::OUTPUT_LEVEL_STANDARD, "server", aBuf);
m_aClients[ClientID].m_State = CClient::STATE_INGAME;
SendServerInfo(ClientID);
GameServer()->OnClientEnter(ClientID);
}
}
NETMSG_INPUT
| Sender: | Client |
|---|---|
| Recipient: | Server |
| Message ID: | 20 |
| Response to: | Sent on changed user input |
| Expected response: | NETMSG_INPUTTIMING |
| Argument name | Type | Note |
|---|---|---|
| Ack Game Tick | Int | Informs the server it can now use the snapshot with this game tick as base for new delta snapshots. |
| Prediction Tick | Int | TODO |
| Size | Int |
Size in bytes of the CNetObj_PlayerInput struct.
The client uses sizeof(CNetObj_PlayerInput) to calculate this size.
Since all fields of the struct are integers and integers are expected to be 4 bytes in C++
this size is 4 times bigger than the amount of integers that are being sent.
So until someone changes the layout of the CNetObj_PlayerInput
struct
here
this value will always be 40 and the
data field will be in the message
10 times.
|
| [data] Direction | Int |
m_Direction of the
CNetObj_PlayerInput struct. Indicating the direction the tee wants to walk in.
|
| [data] TargetX | Int |
m_TargetX of the
CNetObj_PlayerInput struct. X coordinate of the tees cursor. The coordinate is not absolute in the world but relative to the tee. The tee being the origin 0,0 and aiming left would be a negative x coordinate and aiming right would be a positive x coordinate. |
| [data] TargetY | Int |
m_TargetY of the
CNetObj_PlayerInput struct. Y coordinate of the tees cursor. The coordinate is not absolute in the world but relative to the tee. The tee being the origin 0,0 and aiming up would be a negative y coordinate and aiming down would be a positive y coordinate. |
| [data] Jump | Int |
m_Jump of the
CNetObj_PlayerInput struct.
|
| [data] Fire | Int | m_Fire of the CNetObj_PlayerInput struct. |
| [data] Hook | Int |
m_Hook of the
CNetObj_PlayerInput struct.
|
| [data] PlayerFlags | Int | m_PlayerFlags of the CNetObj_PlayerInput struct. |
| [data] WantedWeapon | Int | m_WantedWeapon of the CNetObj_PlayerInput struct. |
| [data] NextWeapon | Int | m_NextWeapon of the CNetObj_PlayerInput struct. |
| [data] PrevWeapon | Int | m_PrevWeapon of the CNetObj_PlayerInput struct. |
| Ping Correction | Int | TODO |
When is NETMSG_INPUT sent
The server assumes the input is held if no input message updates the state. So the official client also keeps the network bandwith minimal and does not resend this message if a key is held.But if the client is active and in game it sends inputs at least in 10hz intervals
// send at at least 10hz
if(time_get() > s_LastSendTime + time_freq()/25)
Send = true;
While the client is in the menu. Empty inputs will be send every second.
// we freeze the input if chat or menu is activated
if(m_pClient->m_pChat->IsActive() || m_pClient->m_pMenus->IsActive())
{
OnReset();
mem_copy(pData, &m_InputData, sizeof(m_InputData));
// send once a second just to be sure
if(time_get() > s_LastSendTime + time_freq())
Send = true;
}
What is sent in NETMSG_INPUT
The message always contains 4 simple Integer fields: Ack Game Tick, Prediction Tick, Size, Ping correction.And then there is Size / 4 amount of data fields between the Size field and the Ping correction field. The official client is using a CNetObj_PlayerInput struct to store the users key presses. All fields are integers so every field in the struct will become one data field in the NETMSG_INPUT message.
struct CNetObj_PlayerInput
{
int m_Direction;
int m_TargetX;
int m_TargetY;
int m_Jump;
int m_Fire;
int m_Hook;
int m_PlayerFlags;
int m_WantedWeapon;
int m_NextWeapon;
int m_PrevWeapon;
};
What does the server reply to NETMSG_INPUT
The server unpacks this message in CServer::ProcessClientPacket(CNetChunk *pPacket) and replys with NETMSG_INPUTTIMING
else if(Msg == NETMSG_INPUT)
{
CClient::CInput *pInput;
int64 TagTime;
int64 Now = time_get();
m_aClients[ClientID].m_LastAckedSnapshot = Unpacker.GetInt();
int IntendedTick = Unpacker.GetInt();
int Size = Unpacker.GetInt();
// check for errors
if(Unpacker.Error() || Size/4 > MAX_INPUT_SIZE)
return;
if(m_aClients[ClientID].m_LastAckedSnapshot > 0)
m_aClients[ClientID].m_SnapRate = CClient::SNAPRATE_FULL;
// add message to report the input timing
// skip packets that are old
if(IntendedTick > m_aClients[ClientID].m_LastInputTick)
{
int TimeLeft = ((TickStartTime(IntendedTick)-Now)*1000) / time_freq();
CMsgPacker Msg(NETMSG_INPUTTIMING, true);
Msg.AddInt(IntendedTick);
Msg.AddInt(TimeLeft);
SendMsg(&Msg, 0, ClientID);
}
NETMSG_RCON_CMD
| Sender: | Client |
|---|---|
| Recipient: | Server |
| Message ID: | 21 |
| Response to: | Sent when the client submits a rcon command |
| Expected response: |
[ NETMSG_RCON_LINE ] | [ NETMSG_RCON_AUTH_OFF logout ] | [ NETMSG_SERVERINFO sv_name, password, sv_max_clients ] | [ NETMSGTYPE_SV_SERVERSETTINGS sv_vote_kick (and more)
]
|
| Argument name | Type | Note |
|---|---|---|
| Command | String | The rcon command like for example status or shutdown |
Sent by the client using the CClient::Rcon(const char *pCmd) method.
void CClient::Rcon(const char *pCmd)
{
CMsgPacker Msg(NETMSG_RCON_CMD, true);
Msg.AddString(pCmd, 256);
SendMsg(&Msg, MSGFLAG_VITAL);
}
NETMSG_RCON_AUTH
| Sender: | Client |
|---|---|
| Recipient: | Server |
| Message ID: | 22 |
| Response to: | Sent on user input (password attempt in console) |
| Expected response: |
NETMSG_RCON_AUTH_ON | NETMSG_RCON_LINE (wrong password/no password set) | NET_CTRLMSG_CLOSE (Too many remote console authentication tries) |
| Argument name | Type | Note |
|---|---|---|
| Password | String |
The password has to match either
sv_rcon_password
or
sv_rcon_mod_password
to successfully authenticate. If both are set to an empty string ""
users can not authenticate.
|
No encryption
Since the field type is a normal String the password is sent as plaintext. Which shows up as a fully readable string when looking at the network traffic.Weak bruteforce protection
Clients can send this packet up tosv_rcon_max_tries (default 3) times.
But it is tracked per client not per ip. So one user with one ip
can attempt (sv_max_clients_per_ip x sv_rcon_max_tries)
passwords without reconnecting. Which is 4 x 3 = 12 by default.
Reconnecting then resets the whole client data including the rcon attempt counter
so you get sv_rcon_max_tries again. Note that reconnecting takes some
time and the server kicks ips that reconnect too fast for 1 minute.
Sent by the client in CClient::RconAuth()
void CClient::RconAuth(const char *pName, const char *pPassword)
{
if(RconAuthed())
return;
CMsgPacker Msg(NETMSG_RCON_AUTH, true);
Msg.AddString(pPassword, 32);
SendMsg(&Msg, MSGFLAG_VITAL);
}
NETMSG_REQUEST_MAP_DATA
| Sender: | Client |
|---|---|
| Recipient: | Server |
| Message ID: | 23 |
| Response to: |
NETMSG_MAP_CHANGE (download start) | NETMSG_MAP_DATA (continue download) |
| Expected response: | NETMSG_MAP_DATA |
| Argument name | Type | Note |
|---|---|---|
| None | ||
sv_map_download_speed (default 8)
NETMSG_MAP_DATA chunks the client has to request
more by sending this message.
Sent to kickstart the download on NETMSG_MAP_CHANGE in CClient::ProcessServerPacket()
// request first chunk package of map data
CMsgPacker Msg(NETMSG_REQUEST_MAP_DATA, true);
SendMsg(&Msg, MSGFLAG_VITAL|MSGFLAG_FLUSH);
And also in
CClient::ProcessServerPacket()
on NETMSG_MAP_DATA to keep the download going
// request next chunk package of map data
CMsgPacker Msg(NETMSG_REQUEST_MAP_DATA, true);
SendMsg(&Msg, MSGFLAG_VITAL|MSGFLAG_FLUSH);
NETMSG_AUTH_START
| Sender: | Unused |
|---|---|
| Recipient: | Unused |
| Message ID: | 24 |
| Response to: | Unused |
| Expected response: | Unused |
| Argument name | Type | Note |
|---|---|---|
| None | ||
NETMSG_AUTH_RESPONSE
| Sender: | Unused |
|---|---|
| Recipient: | Unused |
| Message ID: | 25 |
| Response to: | Unused |
| Expected response: | Unused |
| Argument name | Type | Note |
|---|---|---|
| None | ||
NETMSG_PING
| Sender: | Client |
|---|---|
| Recipient: | Server |
| Message ID: | 26 |
| Response to: | Triggerd client side by the ping console command |
| Expected response: | NETMSG_PING_REPLY |
| Argument name | Type | Note |
|---|---|---|
| None | ||
NETMSG_PING_REPLY
| Sender: | Client Server |
|---|---|
| Recipient: | Client |
| Message ID: | 27 |
| Response to: | NETMSG_PING |
| Expected response: | None |
| Argument name | Type | Note |
|---|---|---|
| None | ||
NETMSG_ERROR
| Sender: | Unused |
|---|---|
| Recipient: | Unused |
| Message ID: | 28 |
| Response to: | Unused |
| Expected response: | Unused |
| Argument name | Type | Note |
|---|---|---|
| None | ||
NETMSG_MAPLIST_ENTRY_ADD
| Sender: | Server |
|---|---|
| Recipient: | Client |
| Message ID: | 29 |
| Response to: | NETMSG_RCON_AUTH |
| Expected response: | None |
| Argument name | Type | Note |
|---|---|---|
| Map name | String | Name of the map that should be added to the clients autocompletion list |
Similar to the rcon command autocompletion in the clients remote console (NETMSG_RCON_CMD_ADD). This sends autocompletion for the argument of the rcon commands
sv_map and change_map.
The server sends every map entry from its map folder to the clients that authenticated in the rcon console.
Admininistrators and moderators can then type sv_map into the remote console
and see/autocomplete the list of possible maps.
NETMSG_MAPLIST_ENTRY_REM
| Sender: | [Server] |
|---|---|
| Recipient: | Client |
| Message ID: | 30 |
| Response to: | Unused |
| Expected response: | None |
| Argument name | Type | Note |
|---|---|---|
| Map name | String | Name of the map that should be removed from the clients autocompletion list |
Counter part to NETMSG_MAPLIST_ENTRY_ADD. Removing map names from the autocompletion list. There is code in the server that can send this message and there is code in the client that removes the entry. But it is never run. So this message is technically unused (for now).
